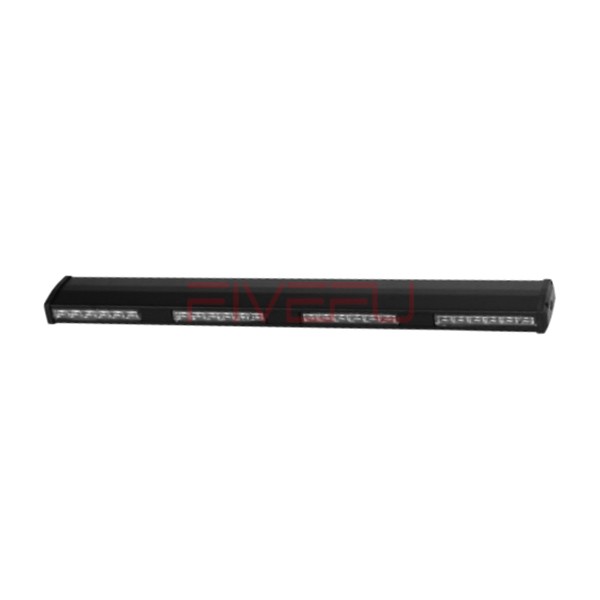
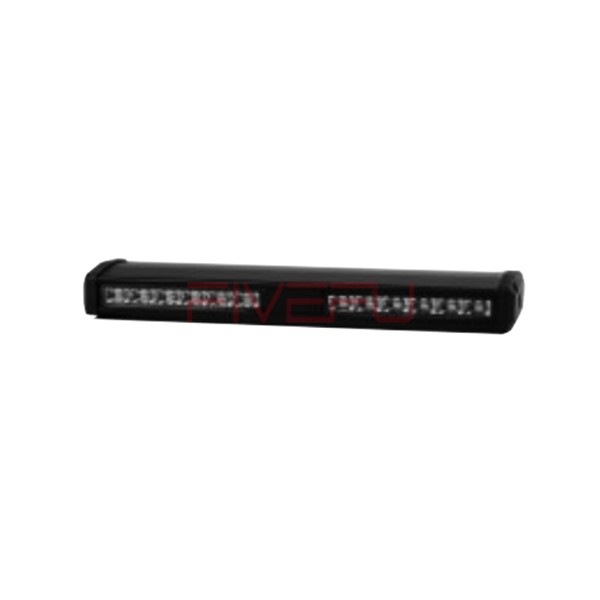
Introduction:
Vehicle warning lights are subject to various regulations that govern their design, use, and performance standards. These regulations ensure that the lights are effective and safe for use on public roads and in emergency situations. Understanding these regulations is crucial for manufacturers and users to ensure compliance and optimal functionality.
Key Regulatory Bodies and Standards:
SAE International (Society of Automotive Engineers)
SAE Standards: These are primarily used in the United States and dictate specifications such as the intensity, color, and pattern of the lights. SAE standards like J845, J595, and J2498 outline requirements for optical warning devices for authorized emergency, maintenance, and service vehicles.
ECE Regulations (Economic Commission for Europe)
ECE R65 and R10: Widely recognized in Europe, these regulations specify the requirements for the homologation of warning lights. ECE R65 covers the photometric and colorimetric properties, while ECE R10 deals with electromagnetic compatibility.
Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards (FMVSS)
FMVSS 108: In the U.S., this standard outlines the requirements for automotive lighting, signaling, and reflective devices. It includes specifications for the installation and performance of warning lights on vehicles.
Specific Requirements:
Color Specifications: Different colors are designated for specific types of services. For example, red lights are typically used by fire and police vehicles, blue by police, and amber for road service or maintenance vehicles.
Visibility and Intensity: Regulations stipulate how visible the lights must be from certain distances and angles, and under various weather conditions.
Flash Patterns: Certain patterns are regulated to avoid confusion and ensure recognition by the public.
Location and Mounting: There are guidelines on where lights can be mounted on vehicles to ensure maximum visibility without compromising safety or vehicle operation.
Regional Variations:
Regulations can vary significantly by country and region, with each jurisdiction potentially having unique requirements based on local road conditions and legal frameworks.
It’s essential for manufacturers and operators to be aware of local regulations in addition to international standards if they operate across different regions.
Compliance and Enforcement:
Vehicles equipped with warning lights must often be approved through a certification process that ensures compliance with the relevant standards.
Regular inspections and audits may be conducted by authorities to ensure ongoing compliance.
Conclusion:
Regulations for vehicle warning lights are critical for ensuring that these devices perform their roles effectively, maintaining road safety and aiding in emergency responses. Manufacturers need to design products according to these strict standards, and users must install and operate them in compliance with legal requirements to ensure safety and legality in their operations.